SpringMVC
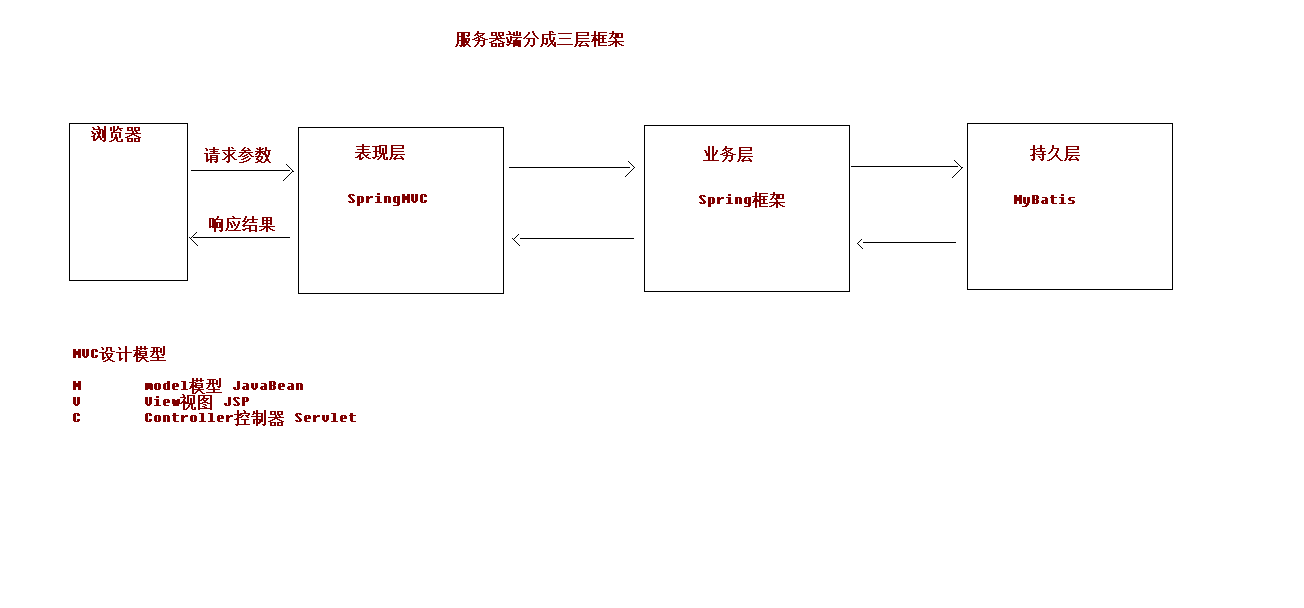
三层架构
表现层
也就是我们经常说的web层。它负责接收客户端请求,向客户端响应结果,通常客户端使用http协议请求web层,web需要接收http请求,完成http响应。
表现层包括展示层和控制层:控制层负责接收请求,展示层负责结果的展示。
表现层依赖业务层,接收到客户端请求一般会调用业务层进行业务处理,并将处理结果响应给客户端。
表现层的设计一般都使用MVC模型。(MVC只是表现层的设计模型,和其它层没有关系)
业务层
也就是我们经常说的service层。它负责业务逻辑的处理,和我们开发项目的需求息息相关。web层依赖业务层,但是业务层不依赖web层。
业务在业务处理时可能会依赖持久层,如果要对数据持久化需要保证事务一致性。(也就是我们说的,事务应该放到业务层来控制)
持久层
也就是我们经常说的dao层。负责数据持久化,包括数据层即数据访问层,数据库是对数据进行持久化的载体,数据访问层是业务层和持久层交互的接口,业务层需要通过数据访问层将数据持久化到数据库中。通俗的讲,持久层就是和数据库交互,对数据库进行增删改查的。
MVC模型
MVC全名是Model View Controller,是模型(model),视图(view),控制器(Controller)的缩写,是一种用于设计创建Web应用程序表现层的模式。MVC中每个部分各司其职:
Model(模型):
通常指的就是我们的数据模型。作用一般情况下用于封装数据。
View(视图):
通常指的就是我们的Jsp或者html。作用一般就是展示数据的。
通常视图时依据模型数据创建的。
Controller(控制器):
是应用程序中处理用户交互的部分。作用一般就是处理程序逻辑的。
SpringMVC在三层架构中的位置
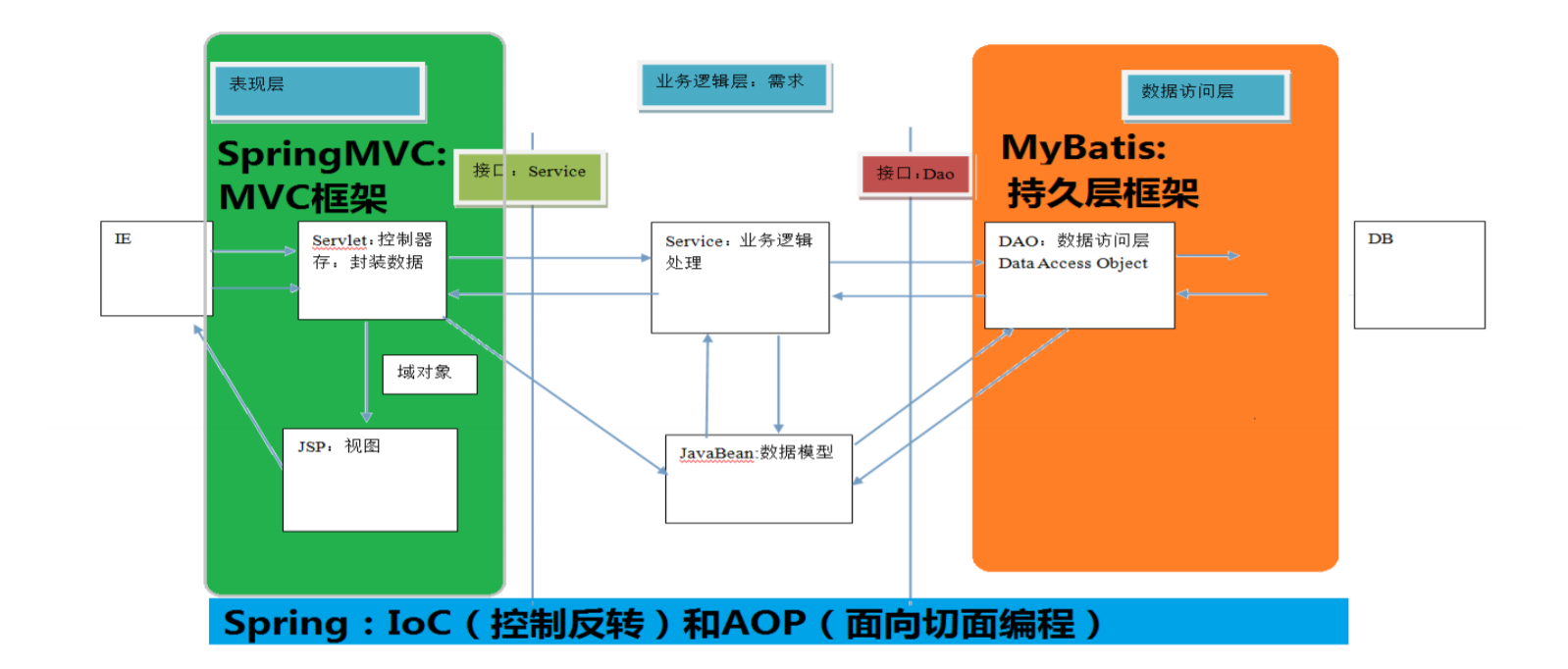
SpringMVC的优势:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| 1、清晰的角色划分:
前端控制器(DispatcherServlet)
请求到处理器映射(HandlerMapping)
处理器适配器(HandlerAdapter)
视图解析器(ViewResolver)
处理器或页面控制器(Controller)
验证器( Validator)
命令对象(Command 请求参数绑定到的对象就叫命令对象)
表单对象(Form Object 提供给表单展示和提交到的对象就叫表单对象)。
2、分工明确,而且扩展点相当灵活,可以很容易扩展,虽然几乎不需要。
3、由于命令对象就是一个 POJO,无需继承框架特定 API,可以使用命令对象直接作为业务对象。
4、和 Spring 其他框架无缝集成,是其它 Web 框架所不具备的。
5、可适配,通过 HandlerAdapter 可以支持任意的类作为处理器。
6、可定制性,HandlerMapping、ViewResolver 等能够非常简单的定制。
7、功能强大的数据验证、格式化、绑定机制。
8、利用 Spring 提供的 Mock 对象能够非常简单的进行 Web 层单元测试。
9、本地化、主题的解析的支持,使我们更容易进行国际化和主题的切换。
10、强大的 JSP 标签库,使 JSP 编写更容易。
………………还有比如RESTful风格的支持、简单的文件上传、约定大于配置的契约式编程支持、基于注解的零配
置支持等等。
|
SpringMVC和Struts2的优略分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| 共同点:
它们都是表现层框架,都是基于 MVC 模型编写的。
它们的底层都离不开原始 ServletAPI。
它们处理请求的机制都是一个核心控制器。
区别:
Spring MVC 的入口是 Servlet, 而 Struts2 是 Filter
Spring MVC 是基于方法设计的,而 Struts2 是基于类,Struts2 每次执行都会创建一个动作类。所
以 Spring MVC 会稍微比 Struts2 快些。
Spring MVC 使用更加简洁,同时还支持 JSR303, 处理 ajax 的请求更方便
(JSR303 是一套 JavaBean 参数校验的标准,它定义了很多常用的校验注解,我们可以直接将这些注
解加在我们 JavaBean 的属性上面,就可以在需要校验的时候进行校验了。)
Struts2 的 OGNL 表达式使页面的开发效率相比 Spring MVC 更高些,但执行效率并没有比 JSTL 提
升,尤其是 struts2 的表单标签,远没有 html 执行效率高。
|
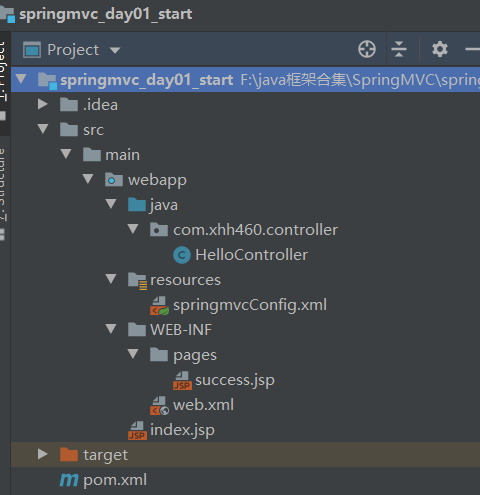
入门案例:
项目目录:
pom.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.xhh460</groupId>
<artifactId>springmvc_day01_start</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>springmvc_day01_start Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<spring.version>5.0.2.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>springmvc_day01_start</finalName>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
|
src\main\webapp\WEB-INF\web.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvcConfig.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
|
com.xhh460.controller.HelloController.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| package com.xhh460.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(path = "/hello")
public String sayHello(){
System.out.println("Hello SpringMVC");
return "success";
}
}
|
src\main\webapp\resources\springmvcConfig.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:contexn="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<contexn:component-scan base-package="com.xhh460"/>
<bean id="internalResourceViewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
</beans>
|
src\main\webapp\index.jsp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| <%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: coderYang
Date: 2021/1/31
Time: 16:45
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3 style="color: red">入门程序</h3>
<a href="hello">点击</a>
</body>
</html>
|
src\main\webapp\WEB-INF\pages\success.jsp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: coderYang
Date: 2021/1/31
Time: 17:03
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="color: green">恭喜你入门了</h1>
</body>
</html>
|
执行过程分析
- 当启动Tomcat服务器的时候,因为配置了load-on-startup标签,所以会创建DispatcherServlet对象,就会加载springmvc.xml配置文件。
- 开启了注解扫描,那么HelloController对象就会被创建。
- 从index.jsp发送请求,请求会先到达DispatcherServlet核心控制器,根据配置@RequestMapping注解找到执行的具体方法。
- 根据执行方法的返回值,再根据配置的视图解析器,去指定的目录下查找指定名称的JSP文件。
- Tomcat服务器渲染页面,做出响应。
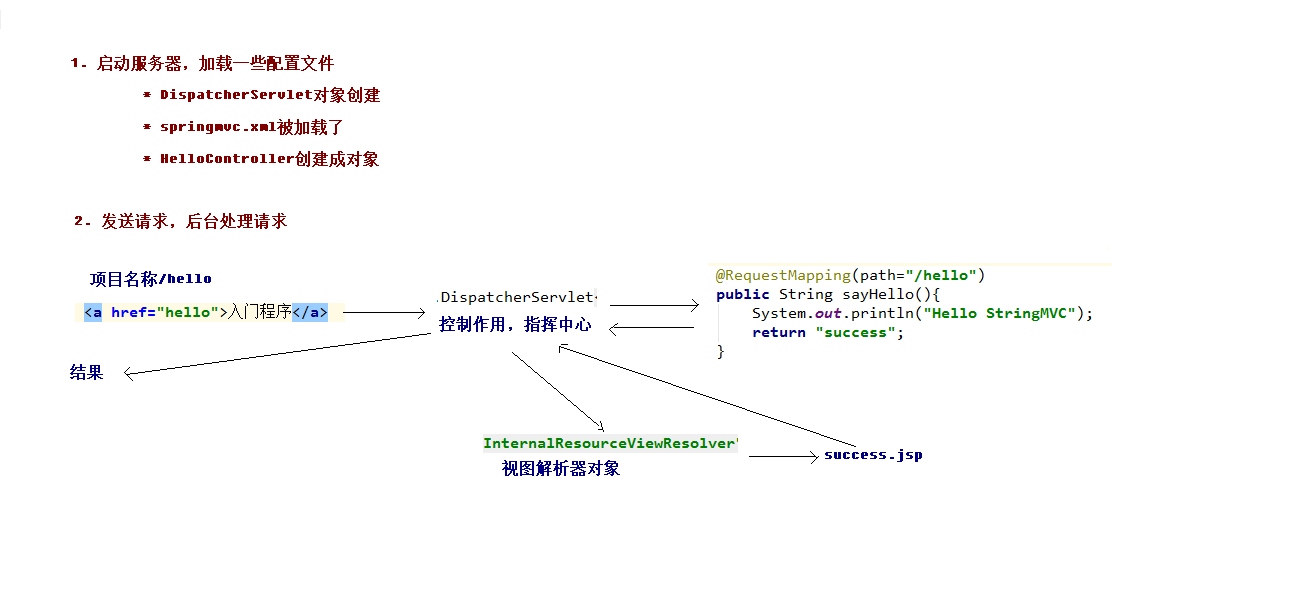
springmvc基于组件方式执行流程
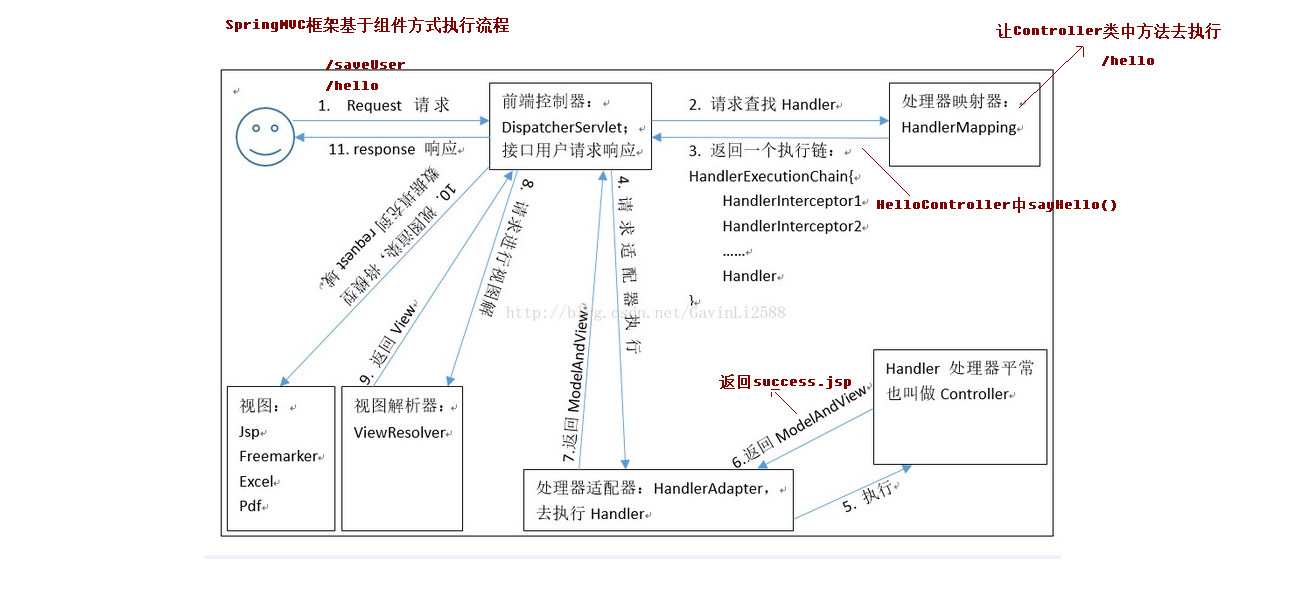
DispatcherServlet:前端控制器
用户请求达到前端控制器,它就相当于mvc模式中的c,dispatcherServlet是整个流程控制的中心,由它调用其它组件处理用户的请求,dispatcherServlet的存在降低了组件之间的耦合性。
HandlerMapping:处理映射器
HandlerMapping负责根据用户请求找到Handler即处理器,SpringMVC提供了不同的映射器实现不同的映射方式,例如:配置文件方式,实现接口方式,注解方式等。
Handler:处理器
它就是我们开发中要编写的具体业务控制器。由DispatcherServlet把用户请求转发到Handler。由Hanlder对用户请求进行处理。
HandlerAdapter:处理适配器
通过HandlerAdaper对处理器进行执行,这是适配器的应用,通过扩展适配器可以对更多类型的处理器执行。
View Resolver:视图解析器
View Resolver负责将处理结果生成View视图类型的支持,包括:jstlView、freemarkerView、pdfView等。我们最常用的视图就是jsp。
一般情况下需要通过页面标签或页面模版技术将模型数据通过页面展示给用户,需要由程序员根据业务需求开 发具体的页面。
<mvc:annotation-driven>说明
在 SpringMVC 的各个组件中,处理器映射器、处理器适配器、视图解析器称为 SpringMVC 的三大组件。 使 用 自动加载 RequestMappingHandlerMapping (处理映射器) 和 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter ( 处 理 适 配 器 ) , 可 用 在 SpringMVC.xml 配 置 文 件 中 使 用 替代注解处理器和适配器的配置。 它就相当于在 xml 中配置了:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerM
apping"></bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping"></bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerA
dapter"></bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter"></bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter"></bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExcept
ionResolver"></bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolv
er"></bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver"
></bean>
|
RequestMapping





